The history of meteorological satellites at JMA
GMS (Geostationary Metrological satellite) series
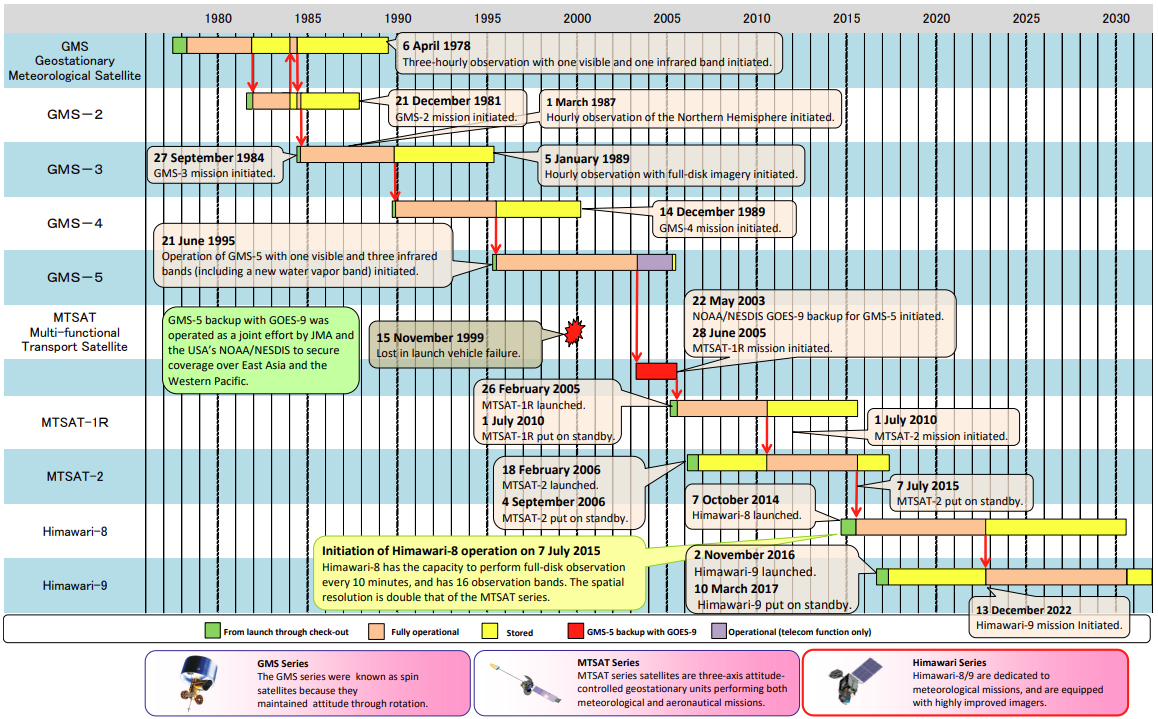
The Geostationary Meteorological Satellite (GMS) series is operated by JMA as part of the Global System of Meteorological Satellites. The first GMS was launched in July 1977, and operational provision of meteorological products created with data from the satellite was commenced on April 6 1978. Its successors, referred to as GMS-2, 3, 4 and 5, were launched in August 1981, August 1984, September 1989 and March 1995, respectively.
| GMS (Himawari) | Launch date: 14 June 1977 Retirement: June 1989 Launch site: Cape Canaveral |
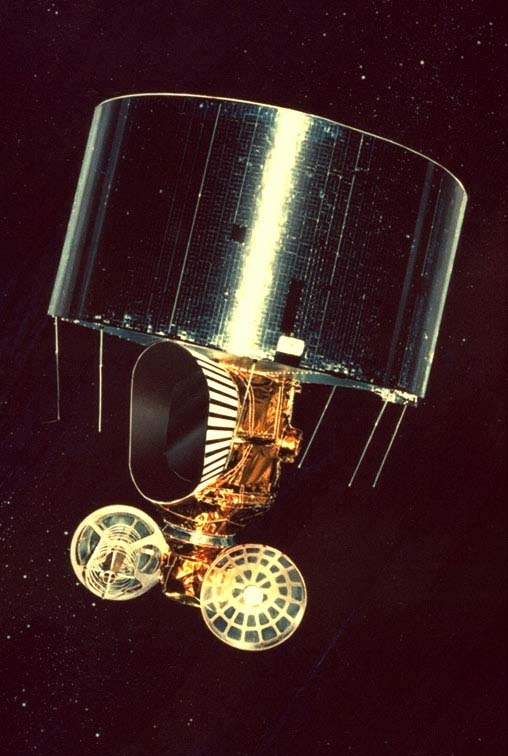 |
|---|---|---|
| GMS-2 (Himawari-2) | Launch date: 11 August 1981 Retirement: November 1987 Launch site: Tanegashima |
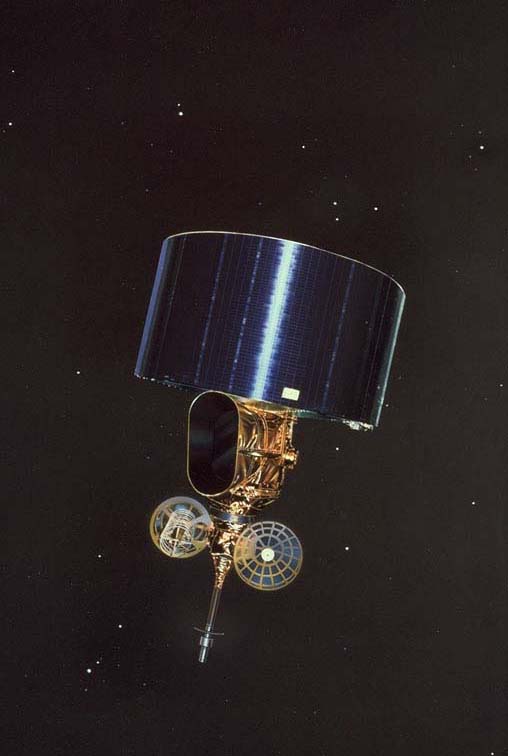 |
| GMS-3 (Himawari-3) | Launch date: 3 August 1984 Retirement: June 1995 Launch site: Tanegashima |
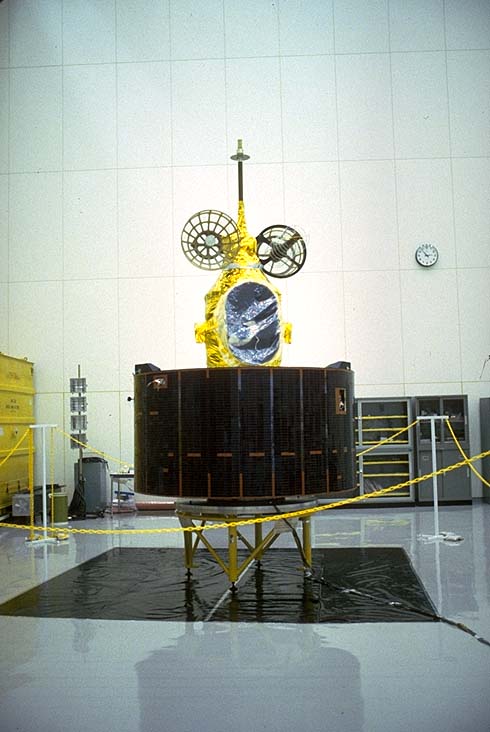 |
| GMS-4 (Himawari-4) | Launch date: 6 September 1989 Retirement: February 2000 Launch site: Tanegashima |
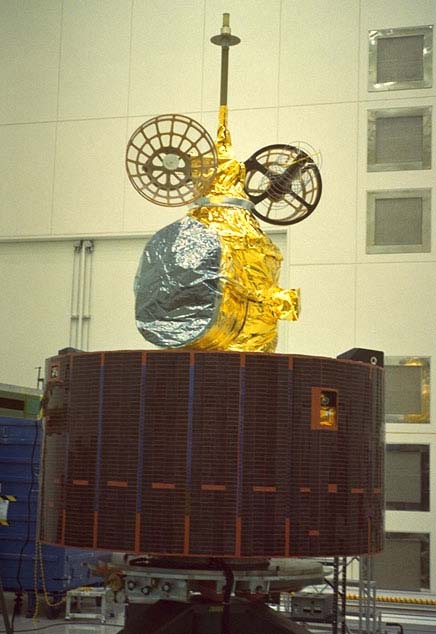 |
| GMS-5 (Himawari-5) | Launch date: 18 March 1995 Retirement: July 2005 Launch site: Tanegashima |
 |
GMS-series images courtesy of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
MTSAT (Multi-functional Transport Satellite) series
The Multi-functional Transport Satellite (MTSAT) series fulfilled a meteorological function for JMAand an aviation control function for the Civil Aviation Bureau (CAB) of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourisum(MLIT). The MTSAT series succeeded the Geostationary Meteorological Satellite (GMS) series covering East Asia and the Western Pacific. MTSAT-1R and MTSAT-2 meteorological services were discontinued on 23 December 2015 and 10 March 2017, respectively.
MTSAT-1R and MTSAT-2 meteorological services ended on 23 December 2015 and 10 March 2017, respectively.
| MTSAT-1 | Launch date: 15 November 1999 (Launch failure) |
- |
|---|---|---|
| MTSAT-1R (Himawari-6) | Launch date: 26 February 2005 Retirement: December 2015 Launch site: Tanegashima |
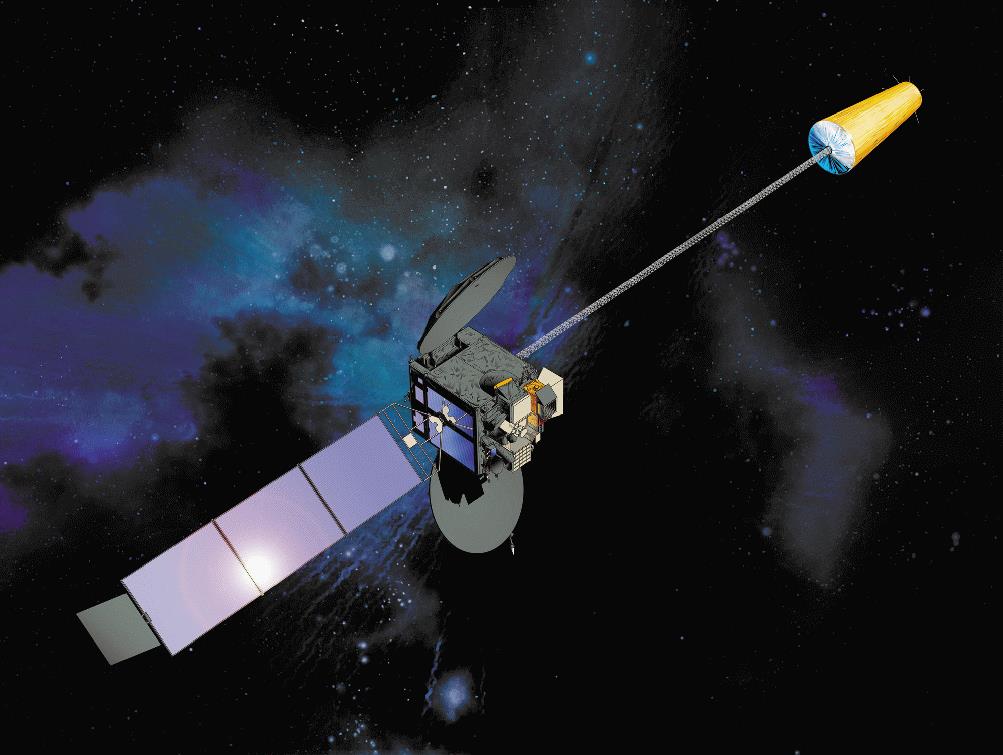 |
| MTSAT-2 (Himawari-7) | Launch date: 18 February 2006 Retirement: March 2017 (Meteorological Mission) Launch site: Tanegashima |
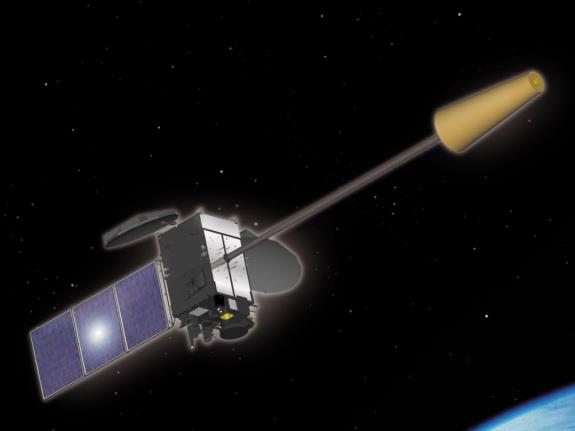 |
Himawari-8/9
Both of JMA's Himawari-8/9 geostationary meteorological satellites (the successors to the MTSAT series) are equipped with highly improved Advanced Himawari Imagers (AHIs). JMA aims to establish a stable and continuous satellite observation system with redundancy based on twin satellite operation involving Himawari-8 and -9, which is expected to contribute to disaster risk reduction in Asia and the western Pacific until JFY2030.
| Himawari-8 | Launch date: 7 October 2014 Stand-by |
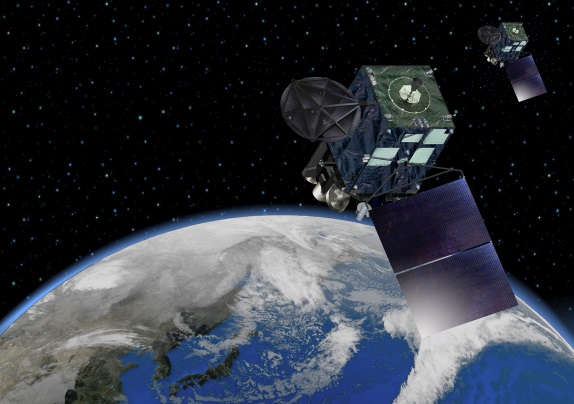 |
|---|---|---|
| Himawari-9 | Launch date: 2 November 2016 Operational |
 |
Channel improvement
| GMS | GMS-2 | GMS-3 | GMS-4 | GMS-5 | MTSAT-1R | MTSAT-2 | Himawari-8 | Himawari-9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Channel and Wavelength |
Visible (0.50-0.70 μm) | Visible (0.55-0.90 μm) | Visible (0.47 μm) Visible (0.51 μm) Visible (0.64 μm) |
||||||
| Near Infrared (0.86 μm) Near Infrared (1.6 μm) Near Infrared (2.3 μm) |
|||||||||
| IR4 (3.5-4.0 μm) | IR (3.9 μm) IR (6.2 μm) IR (6.9 μm) IR (7.3 μm) IR (8.6 μm) IR (9.6 μm) IR (10.4 μm) IR (11.2 μm) IR (12.4 μm) IR (13.3 μm) |
||||||||
| IR3 (6.5-7.0 μm) (Water vapor) |
|||||||||
| IR (Infrared) (10.5-12.5 μm) |
IR1 (10.5-11.5 μm) |
IR1 (10.3-11.3 μm) |
|||||||
| IR2 (11.5-12.5 μm) | |||||||||
Japanese Geostationary Meteorological Satellite Development
Satellite Program Division, Japan Meteorological Agency
E-mail: metsat AT met.kishou.go.jp